前回の続きです。
今回は、MQTTのCONNECTパケットのペイロードから。ペイロードをbinaryパッケージを使って実装します。その後、regexパッケージを使って入力チェック処理を書いてテストします。Goではテストカバレッジが簡単に取得できるようだったので、試しにやってみます。
目次。
CONNECTパケットのペイロード
ペイロードには5つのデータが含まれる。
- Client Identifier
- Will Topic
- Will Message
- UserName
- Password
この中のClient Identifierは必須。残りの4つは可変ヘッダーのConnect Flagsの値次第で必要かどうかが決まる。Connect Flagsについては後回しにしているので、ペイロードでもClient Identifierだけをとりあえずは実装する。
http://docs.oasis-open.org/mqtt/mqtt/v3.1.1/os/mqtt-v3.1.1-os.html#_Toc398718031
Client Identifier
仕様を読むとClient Identifierはこんな感じ。
- クライアント毎にユニーク
- クライアントとサーバー間のセッションを維持するために使う
- ペイロードの先頭
- Section 1.5.3で定義されたUTF-8エンコーディングされた文字列
- さらに条件がある
- 1〜23byte
- 使える文字は
0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ - 以下のように書いてあるけど、許可しないでおく
- 「 The Server MAY allow ClientId’s that contain more than 23 encoded bytes. The Server MAY allow ClientId’s that contain characters not included in the list given above. 」
- 「 A Server MAY allow a Client to supply a ClientId that has a length of zero bytes 」
- 不正なClient Identifierだった場合、サーバーはクライアントにCONNACKパケット(return codeは0x02)を返して、コネクションを切断する
上記の仕様を実装していく。
binaryパッケージ
Client Identifierはペイロードの先頭で、Section 1.5.3で定義されたUTF-8エンコーディングされた文字列なので、ペイロードの先頭の2バイト分がClient Identifierの長さになる。バイト列と数値の変換は binary パッケージが使える。
binary package - encoding/binary - Go Packages
ビッグエンディアンなので、 length := binary.BigEndian.Uint16(payload[0:2]) とすればClient Identifierの長さが取得できる。
package packet import ( "encoding/binary" "github.com/pkg/errors" ) type ConnectPayload struct { ClientID string } func ToConnectPayload(bs []byte) (ConnectPayload, error) { if len(bs) < 3 { return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("payload length is invalid") } length := binary.BigEndian.Uint16(bs[0:2]) var clientID string if len(bs) < 2+int(length) { clientID = string(bs[2:]) } else { clientID = string(bs[2 : 2+length]) } if len(clientID) < 1 || len(clientID) > 23 { return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("ClientID length is invalid") } return ConnectPayload{ClientID: clientID}, nil }
package packet import ( "reflect" "testing" ) func TestToConnectPayload(t *testing.T) { type args struct { bs []byte } tests := []struct { name string args args want ConnectPayload wantErr bool }{ { name: "ClientIDが1文字", args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x01, 'a'}}, want: ConnectPayload{ClientID: "a"}, wantErr: false, }, { name: "ペイロードが0byte", args: args{[]byte{}}, want: ConnectPayload{}, wantErr: true, }, { name: "ClientIDが23文字を超える", args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x18, '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}}, want: ConnectPayload{}, wantErr: true, }, } for _, tt := range tests { t.Run(tt.name, func(t *testing.T) { got, err := ToConnectPayload(tt.args.bs) if (err != nil) != tt.wantErr { t.Errorf("ToConnectPayload() error = %v, wantErr %v", err, tt.wantErr) return } if !reflect.DeepEqual(got, tt.want) { t.Errorf("ToConnectPayload() = %v, want %v", got, tt.want) } }) } }
regexpパッケージ
次は文字の種類をチェック。正規表現を使う。
regexp package - regexp - Go Packages
want: ConnectPayload{},
wantErr: true,
},
+ {
+ name: "使えない文字がある",
+ args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x02, '1', '%'}},
+ want: ConnectPayload{},
+ wantErr: true,
+ },
}
for _, tt := range tests {
t.Run(tt.name, func(t *testing.T) {
--- a/study/packet/connect_payload.go +++ b/study/packet/connect_payload.go @@ -2,6 +2,7 @@ package packet import ( "encoding/binary" + "regexp" "github.com/pkg/errors" ) @@ -10,6 +11,8 @@ type ConnectPayload struct { ClientID string } +var clientIDRegex = regexp.MustCompile("^[a-zA-Z0-9-|]*$") + func ToConnectPayload(bs []byte) (ConnectPayload, error) { if len(bs) < 3 { return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("payload length is invalid") @@ -24,5 +27,8 @@ func ToConnectPayload(bs []byte) (ConnectPayload, error) { if len(clientID) < 1 || len(clientID) > 23 { return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("ClientID length is invalid") } + if !clientIDRegex.MatchString(clientID) { + return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("clientId format shoud be \"0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ\"") + } return ConnectPayload{ClientID: clientID}, nil }
これでOK!
$ go test ./packet/ ok github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet 1.283s
テストのカバレッジ
go test でテストを実行してきたが、オプションをつけるとカバレッジを取得できるらしい。しかも -cover オプションをつけるだけ。
The cover story - The Go Programming Language
試してみる。
$ go test -cover ./packet/ ok github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet 1.270s coverage: 97.6% of statements
97.6%。さっきの文字種類のテストコードを削ってみる。
want: ConnectPayload{},
wantErr: true,
},
- {
- name: "使えない文字がある",
- args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x02, '1', '%'}},
- want: ConnectPayload{},
- wantErr: true,
- },
}
for _, tt := range tests {
t.Run(tt.name, func(t *testing.T) {
実行。
$ go test -cover ./packet/ ok github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet 0.655s coverage: 95.2% of statements
95.2%に下がった。
もっと詳細に調べてみる。 -coverprofile=cover.out という指定をすると、cover.outというファイルができて、そのファイルを go tool cover コマンドでプロファイリングできる。
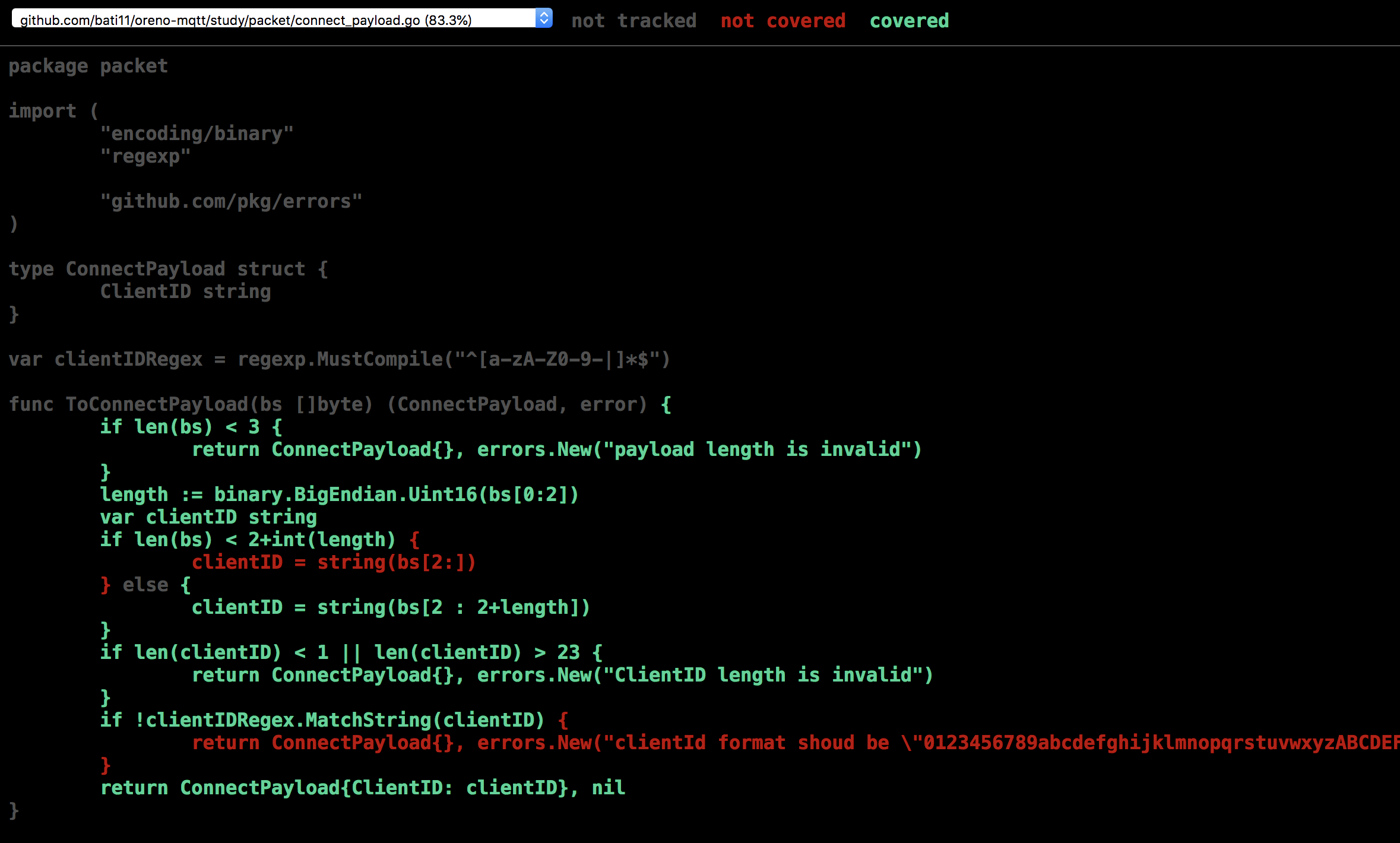
$ go test -coverprofile=cover.out ./packet/ ok github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet 0.019s coverage: 95.2% of statements $ go tool cover -func=cover.out github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_payload.go:16: ToConnectPayload 83.3% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_variable_header.go:23: ToConnectVariableHeader 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_variable_header.go:41: isValidProtocolName 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:14: ToFixedHeader 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:35: refbit 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:40: decodeRemainingLength 100.0% total: (statements) 95.2%
ふむふむ、connect_payload.goの ToConnectPayload のカバレッジが低めだということが分かる。
さらにさらに、 -html=cover.out と指定するとブラウザで確認することもできる。
$ go tool cover -html=cover.out
す、すごい...。
他にも -covermode というオプションがあり、実行された回数まで含めてプロファイルもできそう。
カバレッジ見てたら、指定された長さに対して実際に取得できるClient Identifierの長さが足りない場合のテストが足りないことに気がついたので追加。さっき消したテストも戻す。
--- a/study/packet/connect_payload.go +++ b/study/packet/connect_payload.go @@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ func ToConnectPayload(bs []byte) (ConnectPayload, error) { length := binary.BigEndian.Uint16(bs[0:2]) var clientID string if len(bs) < 2+int(length) { - clientID = string(bs[2:]) + return ConnectPayload{}, errors.New("specified length is not equals ClientID length") } else { clientID = string(bs[2 : 2+length]) }
--- a/study/packet/connect_payload_test.go +++ b/study/packet/connect_payload_test.go @@ -33,6 +33,18 @@ func TestToConnectPayload(t *testing.T) { want: ConnectPayload{}, wantErr: true, }, + { + name: "使えない文字がある", + args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x02, '1', '%'}}, + want: ConnectPayload{}, + wantErr: true, + }, + { + name: "指定された長さよりも実際に取得できたClientIDが短い", + args: args{[]byte{0x00, 0x03, '1', '2'}}, + want: ConnectPayload{}, + wantErr: true, + }, } for _, tt := range tests { t.Run(tt.name, func(t *testing.T) {
go test -coverprofile=cover.out ./packet/ ok github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet 0.022s coverage: 100.0% of statements go tool cover -func=cover.out github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_payload.go:16: ToConnectPayload 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_variable_header.go:23: ToConnectVariableHeader 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/connect_variable_header.go:41: isValidProtocolName 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:14: ToFixedHeader 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:35: refbit 100.0% github.com/bati11/oreno-mqtt/study/packet/fixed_header.go:40: decodeRemainingLength 100.0% total: (statements) 100.0%
$ go test --help を読むと以下のように書いてある。
-cover
Enable coverage analysis.
Note that because coverage works by annotating the source
code before compilation, compilation and test failures with
coverage enabled may report line numbers that don't correspond
to the original sources.
-cover をつけない状態でテストして、PASSしてからカバレッジを取得する方が良さそうだ。
おしまい
MQTTのCONNECTパケットのペイロードを実装して、テストのカバレッジを取得しました。次回はサーバーとして起動するところまでいきたい。
今回の学び